반응형
2178번: 미로 탐색
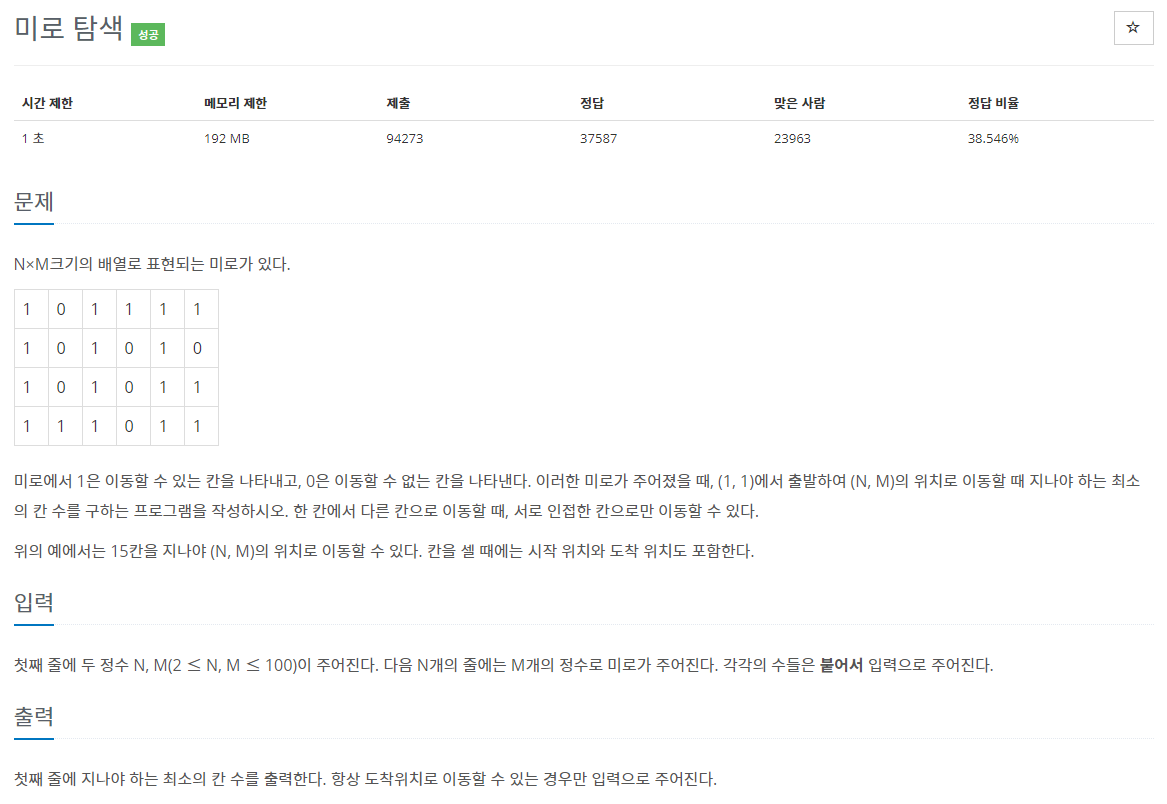
첫째 줄에 두 정수 N, M(2 ≤ N, M ≤ 100)이 주어진다. 다음 N개의 줄에는 M개의 정수로 미로가 주어진다. 각각의 수들은 붙어서 입력으로 주어진다.
www.acmicpc.net
문제 설명

자바 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int n;
static int m;
static int[] dx = { -1, 0, 1, 0 };
static int[] dy = { 0, -1, 0, 1 };
static boolean[][] isVisited;
static int[][] maze;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer strToken=new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
n=Integer.parseInt(strToken.nextToken());
m=Integer.parseInt(strToken.nextToken());
maze=new int[n][m];
isVisited= new boolean[n][m];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
String input=br.readLine();
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
maze[i][j]=input.charAt(j)-'0';
}
}
bfs();
System.out.print(maze[n-1][m-1]);
}
static void bfs(){
LinkedList<Point> queue=new LinkedList<Point>();
queue.add(new Point(0,0));
isVisited[0][0]=true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
Point point=queue.peek();
queue.poll();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nextX=point.x+dx[i];
int nextY=point.y+dy[i];
if(isPossible(nextX,nextY)){
if(!isVisited[nextX][nextY]&&maze[nextX][nextY]!=0){
isVisited[nextX][nextY]=true;
maze[nextX][nextY]=maze[point.x][point.y]+1;
queue.add(new Point(nextX,nextY));
}
}
}
}
}
static boolean isPossible(int nextX,int nextY){
if(nextX<0||nextX>=n){
return false;
}
if(nextY<0||nextY>=m){
return false;
}
return true;
}
static class Point{
int x;
int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
}문제 풀이
최단거리 문제의 경우 대부분 BFS를 이용하면 됩니다.
우선 0,0을 queue에 넣고 이동가능한 칸들을 체크 후 큐에 넣어줍니다.
큐에 넣어 줄때 이동가능한 좌표에 이전좌표값 +1을 하여 거리값을 구합니다.
큐 size가 0이 될때 까지 체크 합니다.
n,m 좌표의 값을 출력하면 됩니다.
반응형
'프로그래밍 > 알고리즘 풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 1003 피보나치 함수 자바 (0) | 2021.07.13 |
|---|---|
| 백준 2606 바이러스 자바 (0) | 2021.07.11 |
| 백준 1697 숨바꼭질 자바 (0) | 2021.07.01 |
| 백준 2667 단지번호붙이기 자바 (0) | 2021.06.27 |
| 백준 1260 DFS와 BFS 자바 (0) | 2021.06.27 |




댓글